Overview
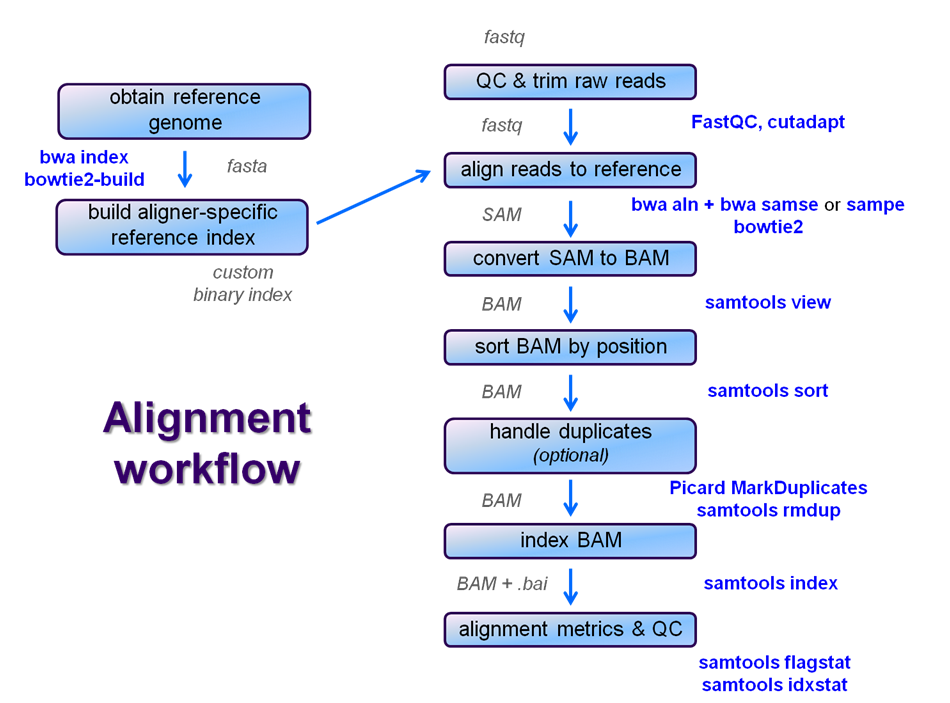 Image Removed
Image Removed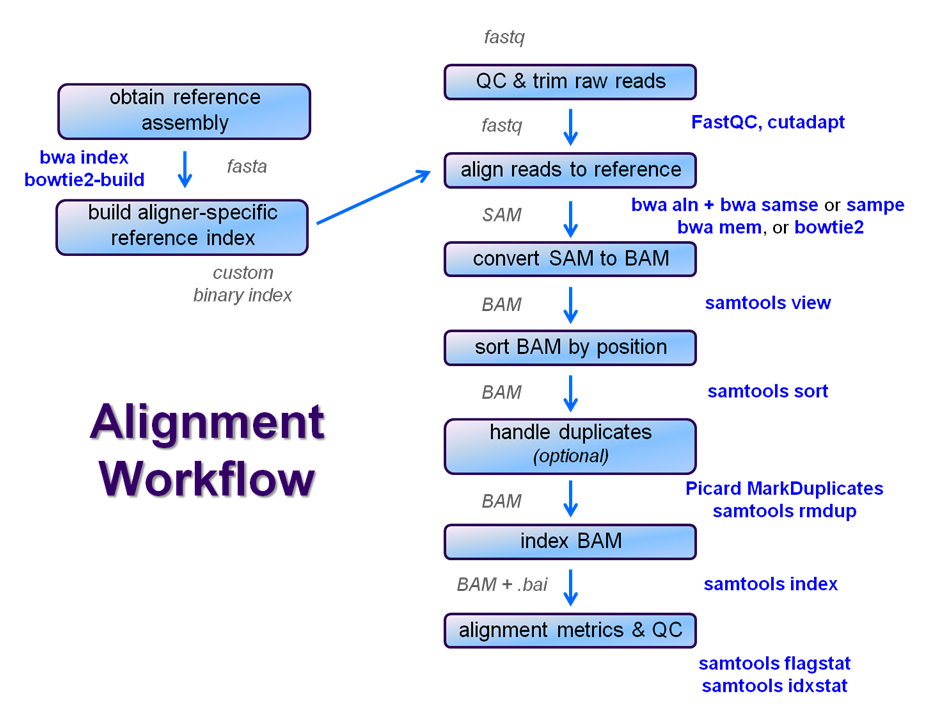 Image Added
Image Added
After raw sequence files are generated (in FASTQ format), quality-checked, and pre-processed in some way, the next step in most NGS pipelines is mapping to a reference genome. For individual sequences, it is common to use a tool like BLAST to identify genes or species of origin. However, a normal NGS dataset will have tens to hundreds of millions of sequences, which BLAST and similar tools are not designed to handle.
...
| Expand |
|---|
|
| There are 1,184,360 alignment records. |
Exercise: How many sequences were in the R1 and R2 FASTQ files combined?
| Expand |
|---|
|
gunzip -c fastq/Sample_Yeast_L005_R1.cat.fastq.gz | echo $((`wc -l` / 2))
|
| Expand |
|---|
|
| There were a total of 1,184,360 original sequences |
Exercises:
- Do both R1 and R2 reads have separate alignment records?
- Does the SAM file contain both aligned and un-aligned reads?
- What is the order of the alignment records in this SAM file?
| Expand |
|---|
|
- Do both R1 and R2 reads have separate alignment records?
- yes, they must, because there were 1,184,360 R1+R2 reads and an equal number of alignment records
- Does the SAM file contain both aligned and un-aligned reads?
- yes, it must, because there were 1,184,360 R1+R2 reads and an equal number of alignment records
- What is the order of the alignment records in this SAM file?
- the names occur in the exact same order as they did in the FASTQ, except that they come in pairs
- the R1 read comes first, then its corresponding R2
- this ordering is called read name ordering
|
...

